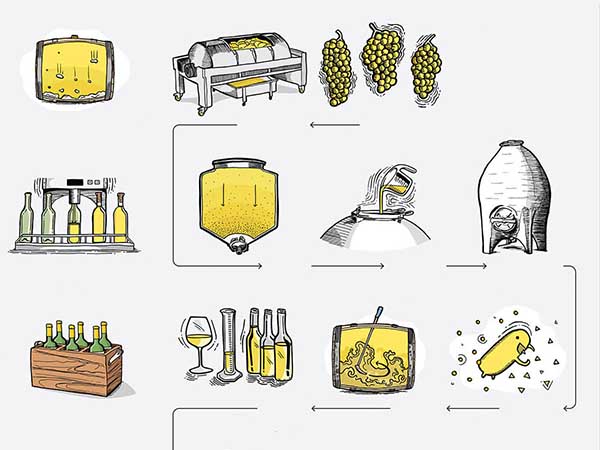
Jak powstaje wino?
• Do sporządzania wina należy używać jedynie w pełni dojrzałych, zdrowych owoców.
• Sok wyciskać bezpośrednio po zmieleniu owoców bądź też – w przypadku ciemnych owoców – przeprowadzić wstępną fermentację w miazdze.
• Nie pozostawiać miazgi zbyt długo bez przykrycia, aby nie dopuścić do rozwoju szkodliwych mikroorganizmów.
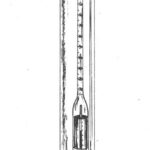
• Określić ciężar moszczu przy pomocy wagi Ochslego: nadające się do użytku wino owocowe powinno wykazać 60° Ochslego.
• Określić kwasowość: całkowita zawartość kwasu w dobrym winie owocowym powinna wynosić 6-8 g/litr.
• Moszcz o zbyt niskiej zawartości cukru dosładza się, dodając cukier kryształ. Aby zwiększyć ciężar moszczu o 1° Ochslego, trzeba na 1 litr dodać 2,6 g cukru.
• Dosładza się jedynie wówczas, gdy moszcz jest zbyt kwaśny (znacznie powyżej 9 g/litr).
• Kwasowość zwiększa się przez kupażowanie z kwaśnym sokiem owocowym albo przez dodanie 80-procentowego kwasu mlekowego.
• Zmniejszenie kwasowości osiąga się przez korygowanie smaku „na mokro” (dodanie wody z cukrem), albo przez dodatek węglanu wapnia; aby obniżyć kwasowość o 1 g na 1 litr, potrzeba 0,7 g węglanu wapnia.
• Wino można uznać za naturalne, jeśli nie były w nim korygowane ani ciężar moszczu, ani zawartość kwasu. Większość win owocowych wymaga jednak korygowania, aby w ogóle nadawały się do picia. Do użytku domowego dozwolone jest korygowanie i dosładzanie aż do osiągnięcia ciężkich win deserowych; nie wolno ich jednak sprzedawać.
• Do fermentacji używa się szklanych balonów (do 50 litrów) oraz plastikowych pojemników (od 100 litrów) albo drewnianych beczek (od 20 litrów).
• Naczynia muszą być czyste i nie skażone pleśnią. Muszą być tak skonstruowane, aby można je było zamknąć za pomocą rurki fermentacyjnej, aby dwutlenek węgla powstający w procesie fermentacji mógł się ulatniać na zewnątrz, natomiast powietrze nie mogło dostać się do środka.
• Temperatura w pomieszczeniu, gdzie odbywa się fermentacja, powinna wynosić 15 – 20°C.
• Podstawowym warunkiem „czystej” fermentacji alkoholowej jest uniemożliwienie rozwoju dzikich drożdży oraz szkodliwych szczepów bakterii; w tym celu dodaje się czyste drożdże winne hodowlane.
• Naczynie fermentacyjne napełnia się tylko do 4/5, aby fermentujący sok mógł rozszerzać swoją objętość.
• Przy ciepłej pogodzie oraz kiedy sok lub miazga nie są całkiem bez zarzutu, można przeprowadzić siarkowanie, dodając pirosiarczyn potasowy w ilości 5- 10 g na 100 litrów.
• Fermentacja jest procesem przemiany i oczyszczenia, powinna więc przebiegać bez zakłóceń.
• Fermentacja jest zakończona, kiedy przestaje się ulatniać dwutlenek węgla, a areometr wskazuje 0° Ochslego. Po krótkim okresie spokoju należy dokonać pierwszego obciągu.
• Po pierwszym obciągu należy ponownie zmierzyć poszczególne wartości i zanotować je.
• Naczynie fermentacyjne napełnia się po szpunt i zamyka rurką fermentacyjną.
• Młode wino musi leżakować w chłodzie: optymalna temperatura 8 -10°C. Wino dojrzewa dalej, staje się jasne i klarowne.
• Następnie nadchodzi czas drugiego obciągu.
• Później można dokonywać dalszych obciągów lub też rozlać wino do butelek. Także w butelce wino dojrzewa, zbliżając się do optymalnego momentu swej dojrzałości, a kiedy go przekroczy, zaczyna stopniowo tracić na wartości. W zależności od rodzaju, rocznika, zawartości alkoholu i kwasu trwa to latami, a przy bardzo ciężkich winach deserowych nawet dziesiątki lat. Słabe wina trzeba wypić już w pierwszym roku, nawet jeśli zostały rozlane do butelek.